We have been asked by many customers to recommend a way to deploy Office 365 applications using Intune so I wanted to make a blog post to show how you can setup your Office deployments using both Pckgr and the Microsoft 365 Apps admin center. This will allow for simple and smooth deployments of Office during Autopilot as well as ongoing patching.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through a complete deployment process using Pckgr:
- Creating a Configuration XML for Microsoft 365 Apps
- Hosting the XML in an Azure Storage Blob
- Deploying the App with a Custom Install String via Pckgr
- A demo of the installation during Autopilot
Step 1: Create a Configuration XML for Microsoft 365 Apps
To tailor the deployment to your organization’s needs, you’ll first create a custom configuration XML file.
- Visit the Office Configuration Tool:
Go to config.office.com and sign in with your Microsoft account. - Customize Your Configuration:
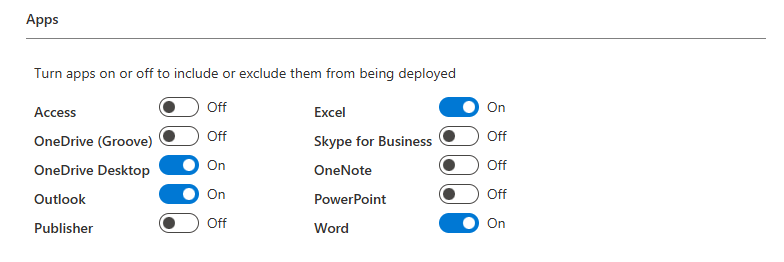
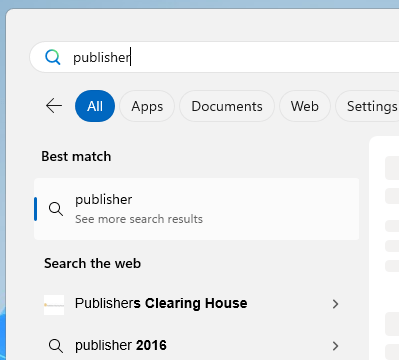
- Select the apps to include (e.g., Word, Excel, PowerPoint). This is a good opportunity to clean up and remove any Office applications that you don’t need on the device. For this demo we have removed less common apps like Publisher and Access. We have also removed Teams so we can manage this deployment via it’s own application.
- Define installation settings such as update channels and application languages. We have set the update channel to Monthly Enterprise as per recommendations from Microsoft
- Set to Automatically accept the EULA
- Provide an organization name for the Office deployment
- Export the XML:
After finalizing your settings, export the configuration as an XML file. This file contains all the specifications needed for a silent, automated deployment.


Step 2: Host the Configuration XML in an Azure Storage Blob
Once you’ve created your XML file, the next step is to host it in a location accessible during deployment.
- Set Up an Azure Storage Account:
- Log in to the Azure portal.
- Create a new storage account or use an existing one.

- Upload the Configuration XML:
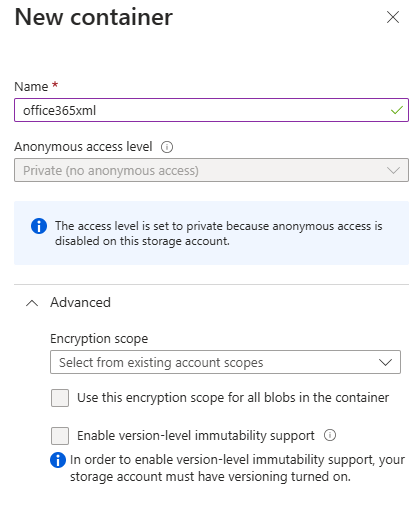
- In your storage account, create a container to host the XML file.
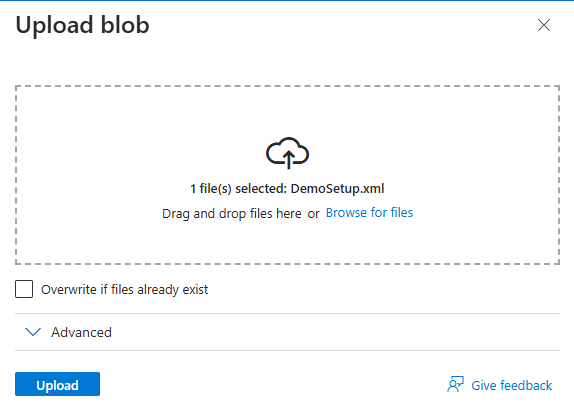
- Upload the XML file to the container.
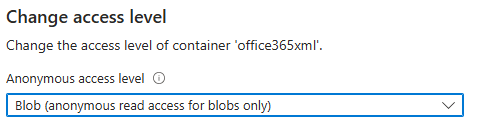
- Configure the container’s access level to allow public or authenticated access, depending on your security requirements. For this example, we are leaving it public. If you leave it private you will also need to provide a SAS token for authorization.
- Note the Blob URL:
Copy the URL of the uploaded XML file. You’ll use this in your Pckgr deployment.

Step 3: Deploy Microsoft 365 Apps Using Pckgr
With the XML configuration hosted, you can now deploy the application through Pckgr.
- Log in to Pckgr Dashboard:
Go to the Pckgr portal and sign in. - Add a New Application:
- Navigate to your application library and select the tenant for deployment.
- Add Microsoft 365 Apps to your library by searching for the application and clicking the “+” button.
- Customize the Deployment String:
- In the deployment settings, use the following custom install
/configure <Azure Blob URL>(Replace<Azure Blob URL>with the URL of your hosted XML file).
- In the deployment settings, use the following custom install
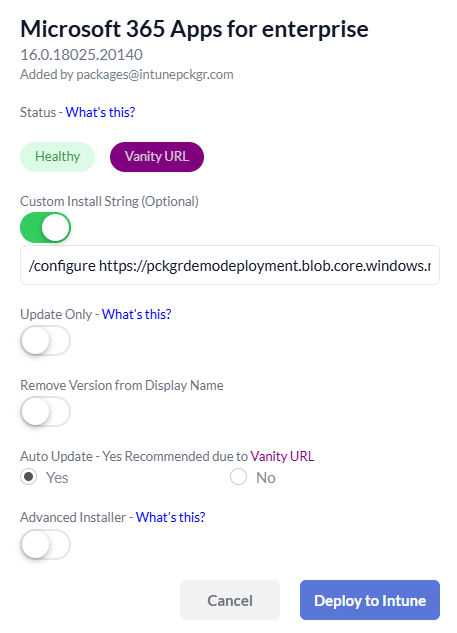
- Deploy to Intune:
- Click the deploy button. Pckgr will package the application as a Win32 app and push it to your Intune tenant.

- Configure Enrolment Status Page (Optional):
- Edit the ESP to include the Office 365 deployment during Autopilot.

Device Install Demo
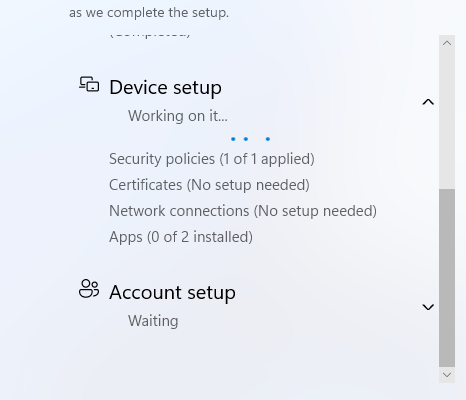
After completing the setup, I wanted to show a demo of the apps installing during Autopilot. Here you can see the package has started installing during the Autopilot ESP. The reason it shows 2 applications is because the Winget Pre-Install also needs to install.
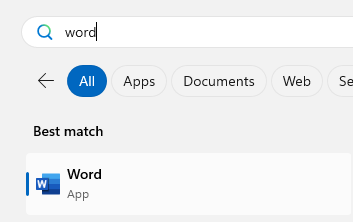
Once the installation completed, we logged into the device to check the install. I was able to confirm Office was installed successfully and that the Template had applied as I was able to find Word but not Publisher (Success!!)
We also checked the Account Settings in Word to confirm the Update Channel is set to Monthly Enterprise.

But what about updates?
When it comes to updating the Office applications, it’s best to leave it to the Update Channel to work its magic. That being said, there are a number of ways that we can apply the update policy which are detailed here: Change the Microsoft 365 Apps update channel for devices in your organization – Microsoft 365 Apps | Microsoft Learn.
I highly recommend leveraging config.office.com to manage the update channels for your Microsoft 365 Apps. This platform allows you to easily configure and switch devices to the Monthly Enterprise Channel, even for devices currently running on the Current Channel. By doing so, you ensure a consistent update settings tailored to your organization’s needs. Additionally, config.office.com provides tools to monitor the status of Office updates across your devices and investigate any reported errors, enabling proactive management and troubleshooting.
Conclusion
If you have made it this far in the blog, thank you for reading and I hope it helped you with managing Office 365 deployments. If you’re not a Pckgr customer, please know we do offer a 30-day trial for any plan which would give you a chance to test out this deployment.
Why Choose Pckgr?
With Pckgr, deploying Microsoft 365 Apps becomes a breeze:
- No Coding Required: Simplify complex packaging tasks without scripts.
- Secure & Tested: Leverage Pckgr’s robust security and testing protocols for error-free deployments.
- Customizable: Use custom XML files to ensure deployments meet your organization’s unique needs.

Leave a comment