In todays blog we are going to look at an error that has frustrated countless IT admins who rely on Winget for installing and updating applications. The dreaded mismatched hash issue. This problem often appears at the worst possible time, usually when you are trying to run a quick command and move on with your day. To help make sense of what is happening, we will break down why this issue occurs, how Winget is designed to protect you, and what you can do when it inevitably pops up. With a bit of context, the next time you see this error you will know exactly how to handle it.
The Scenario
You have just logged into a fresh device and want to quickly install your favourite web browser without manually downloading anything. You open PowerShell and run a Winget command to install Google Chrome, accept the terms, and wait. Instead of a successful installation, you are greeted with an error message and still no browser installed. Now you are forced to open Edge, browse to the official Chrome download page, and run the installer by hand. Not exactly the quick win you were hoping for.
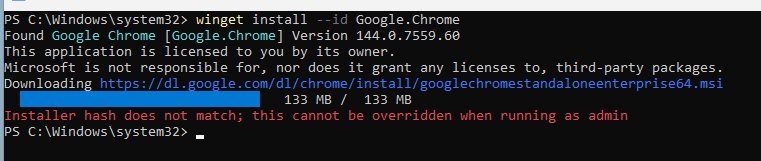
The Issue
To understand what is happening, we need to look at the security protections built into Winget. Microsoft has put several safeguards in place to ensure applications installed through Winget have not been tampered with. When an application or update is submitted to Winget using tools like WingetCreate or Komac, the installer is downloaded from the vendor provided link and a cryptographic hash is calculated. That hash is stored in the Winget manifest and submitted for validation.
Once the manifest is approved, that exact hash becomes the expected value for that installer. When a device later attempts to install the application, Winget downloads the installer from the same link and compares the calculated hash to the one stored in the manifest. If they do not match, the installation is blocked. This is a critical security measure as it prevents malicious actors from swapping out legitimate installers for harmful ones.
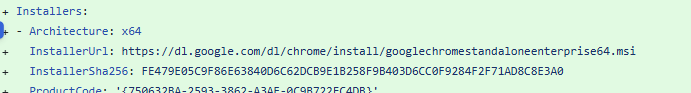
Why this becomes a problem
While this protection is important, it frequently blocks perfectly legitimate installations. Many software vendors, including Google Chrome, use a static download link for their installers. The link itself never changes, but the file behind it does. Each time a new version is released, the installer file is updated and the hash changes.
Because the Winget manifest still expects the old hash, Winget treats the new installer as untrusted and refuses to proceed. Vendors that use version specific download links do not typically run into this issue, since each release has its own unique manifest and hash.
How to confirm this is the cause
When you encounter a mismatched hash error, the first thing to check is whether the vendor has released a newer version of the application. Compare the latest version listed in the vendor release notes with the version currently available in Winget. If the vendor version is newer, there is a very high chance the hash mismatch is the cause of the failure.
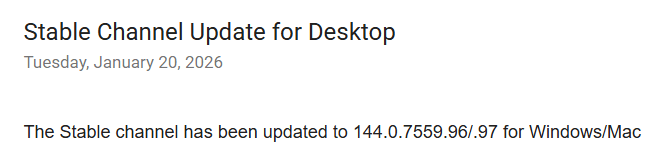

What to do next
Once you have confirmed that a new version has been released, you have a few options. The easiest step is to visit the Winget Community Packages repository on GitHub and check whether a pull request already exists for the updated application. If one is open, there is nothing else to do except wait for it to be reviewed and merged.
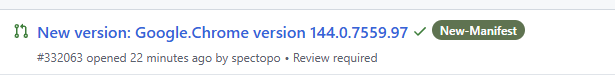
If no update has been submitted yet, you can open an issue in the repository to request one. Alternatively, if you are comfortable with the process, you can submit the updated manifest yourself and help the community move things along faster.
While the mismatched hash issue can be annoying, it is ultimately a sign that Winget is doing its job. With a bit of awareness and a quick check of version changes, you can save yourself time and frustration the next time it appears.

Leave a comment